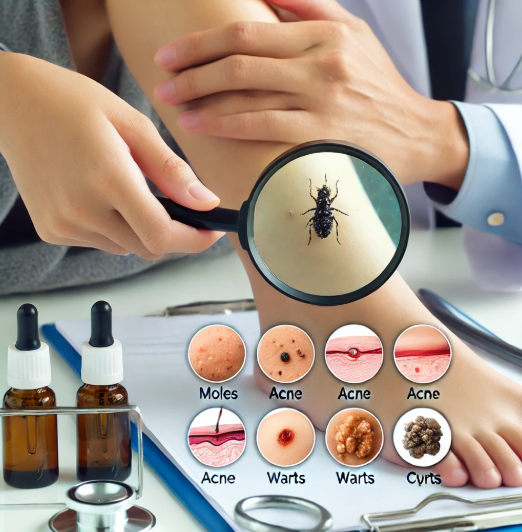
Skin lesions can be caused by various factors, such as infections, skin conditions, or underlying health problems. The treatment for skin lesions depends on the type, cause, and severity of the lesion. Here are some general steps on how to get rid of skin lesions:
1. Consult a Dermatologist
- Diagnosis: The first step in treating skin lesions is consulting a dermatologist for proper diagnosis. A healthcare professional can help determine the type of lesion (e.g., cyst, mole, wart, acne, or an infection).
- Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to rule out skin cancer or other serious conditions.
2. Topical Treatments
- Antibiotic Creams: If the lesion is due to a bacterial infection, antibiotic creams such as Neosporin or Bacitracin may help clear up the infection.
- Antifungal Creams: For fungal infections, over-the-counter antifungal creams like clotrimazole or miconazole can be effective.
- Steroid Creams: Corticosteroid creams may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, particularly for inflammatory conditions like eczema or psoriasis.
- Retinoid Creams: For lesions related to acne or other skin conditions, topical retinoids can help by unclogging pores and promoting skin regeneration.
3. Over-the-Counter Solutions
- Salicylic Acid: For warts or corns, salicylic acid-based treatments can be effective in gradually removing the lesion.
- Tea Tree Oil: Some natural remedies, such as tea tree oil, have antimicrobial properties and may help treat minor lesions like acne or warts.
4. Surgical Options
- Cryotherapy: This procedure uses liquid nitrogen to freeze off certain types of skin lesions, such as warts, moles, and precancerous growths.
- Excision: In cases where the lesion is problematic or suspected to be malignant, a dermatologist may surgically remove the lesion. This is often necessary for suspicious moles or skin cancers.
- Laser Treatment: Laser therapy may be used to treat certain types of skin lesions, such as age spots, sunspots, or tattoos.
5. Home Remedies
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing properties, aloe vera can help reduce inflammation and irritation caused by minor skin lesions.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: It is sometimes used for warts and other minor skin lesions due to its antiseptic properties.
- Honey: Honey has natural antibacterial properties and can be applied to minor cuts or lesions to help prevent infection.
6. Lifestyle and Skin Care Tips
- Sun Protection: Sun exposure can worsen certain skin lesions, so wearing sunscreen and avoiding prolonged exposure to the sun is essential.
- Proper Skin Hygiene: Keeping your skin clean and moisturized can prevent many common skin lesions, especially those caused by bacteria or fungi.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help maintain healthy skin, which may reduce the occurrence of lesions.
7. Treating Underlying Health Conditions
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like psoriasis or lupus can cause chronic skin lesions. Managing the underlying disease with medication or lifestyle changes can help improve skin health.
- Infections: If the lesion is due to a viral infection (e.g., herpes), antiviral medications may be needed.
- Allergies: Skin lesions can sometimes be the result of allergic reactions. Identifying and avoiding triggers, as well as using antihistamines, may help resolve the issue.
8. Avoid Scratching or Picking
- Scratching or picking at skin lesions can cause further irritation, infection, and scarring. It’s important to avoid touching lesions, especially if they are open or infected.
9. Regular Monitoring
- If the lesion does not improve or worsens over time, further medical intervention may be necessary. Regular check-ups can help ensure any serious underlying conditions are detected early.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Help:
- Sudden Changes: If a skin lesion changes in size, shape, or color, it may be a sign of a more serious condition, such as skin cancer.
- Pain or Bleeding: If a lesion becomes painful or starts bleeding uncontrollably, immediate medical attention is advised.
- Infection: If a lesion becomes red, swollen, or develops pus, it may indicate an infection that requires medical treatment.
Conclusion
The approach to getting rid of skin lesions depends on the type of lesion and its cause. Seeking medical advice is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Whether you choose topical treatments, home remedies, or medical interventions, it’s important to follow a proper care plan to avoid further complications and maintain healthy skin.