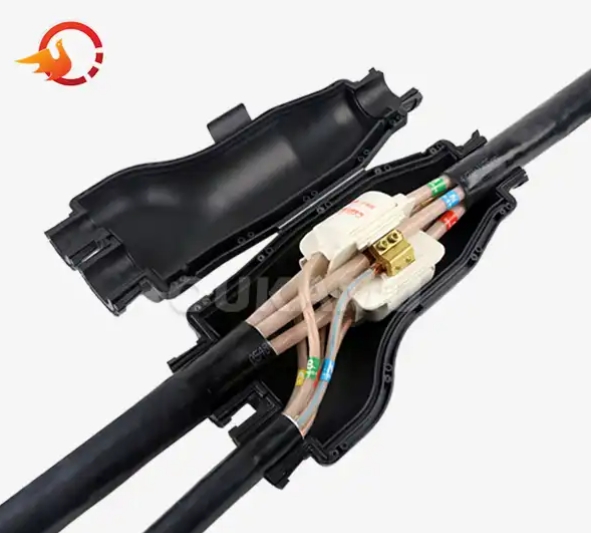
In today’s technology-driven world, branch cables play a crucial role in ensuring efficient connectivity within various infrastructures, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings. These specialized cables, invented by OUKAMU, facilitate seamless cable branch connections, paving the way for improved network performance and reliability. However, like all components of a network, branch cables require regular testing and maintenance to ensure their longevity. This blog will provide insights into how to effectively test and maintain your branch cables, ensuring they serve you well for years to come.
1. What Are the Best Practices for Testing Branch Cables?
Testing branch cables is essential to ensure they are functioning correctly and efficiently. Here are some best practices to follow:
Understanding Cable Specifications
Before testing, familiarize yourself with the specifications of the branch cable you are using. This includes understanding the cable’s capacity, type (e.g., fiber optic, coaxial, or twisted pair), and the environment in which it operates. Each type of cable will have specific testing requirements.
Utilizing Proper Testing Equipment
Invest in high-quality cable testers that can measure continuity, length, and signal quality. Some of the most common types of cable testers include:
(1)Multimeters: Useful for simple continuity tests.
(2)Cable Certifiers: These devices provide detailed reports on cable performance, ensuring they meet industry standards.
(3)Time Domain Reflectometers (TDR): TDRs are excellent for identifying cable faults by sending pulses down the cable and measuring reflections.
Performing Routine Tests
Regular testing should be scheduled, especially in high-traffic areas or environments with heavy machinery. Key tests to perform include:
(1)Continuity Tests: Ensure that all wires within the cable are intact and connected properly.
(2)Signal Quality Tests: Check for any loss in signal quality, which may indicate a problem with the cable.
(3)Length Tests: Confirm that the cable length is within acceptable limits to avoid performance issues.
Documenting Test Results
Keep records of all tests performed, including dates, results, and any corrective actions taken. This documentation will help you track the performance of your branch cables over time and identify any recurring issues.
Conclusion
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your branch cables are operating optimally and are well-maintained, ultimately extending their longevity.
2. How Can You Identify Common Issues with Branch Cables?
Identifying common issues with branch cables is crucial for maintaining their performance and longevity. Below are some of the most frequent problems and how to diagnose them.
Physical Inspection
Start with a physical inspection of the cables. Look for:
(1)Visible Damage: Check for abrasions, cuts, or frayed ends. Any visible damage can significantly affect performance.
(2)Loose Connections: Ensure that all connectors are tightly secured and free of corrosion.
(3)Environmental Conditions: Assess whether the cable is exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, or chemicals that could lead to deterioration.
Signal Loss
Signal loss is a common issue that can stem from various factors:
(1)Cable Length: Longer cables can lead to more significant signal loss. Ensure cables are not longer than the recommended length for their type.
(2)Interference: Electromagnetic interference (EMI) from nearby equipment can degrade signal quality. Ensure that cables are routed away from sources of EMI.
Performance Testing
Use performance testing equipment to identify issues:
(1)Cable Certifiers: These can pinpoint specific problems such as crosstalk and return loss.
(2)TDR: This tool can help locate breaks or faults in the cable.
Troubleshooting Techniques
If you identify a problem, consider these troubleshooting techniques:
(1)Replace Damaged Sections: If a specific section of the cable is damaged, replacing only that part can (2)ften resolve issues without replacing the entire cable.
(3)Re-terminate Connectors: If connectors are corroded or loose, re-terminating them can restore performance.
Conclusion
By being proactive in identifying and addressing common issues, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your branch cables.
3. What Maintenance Practices Ensure the Longevity of Branch Cables?
Maintaining branch cables involves more than just regular testing. Here are some essential maintenance practices that ensure longevity.
Regular Cleaning
Dust and debris can accumulate on connectors and cable surfaces, leading to signal degradation. Implement a regular cleaning schedule using appropriate cleaning solutions and tools.
(1)Connector Cleaning: Use lint-free wipes and isopropyl alcohol to clean the ends of connectors to ensure a good connection.
(2)Cable Cleaning: Wipe down cables with a damp cloth to remove dust and grime.
Proper Cable Management
Good cable management can prevent physical damage and improve airflow around cables. Use cable ties, trays, and conduits to organize cables neatly.
(1)Avoid Sharp Bends: Ensure that cables are not sharply bent, which can cause internal damage.
(2)Labeling: Clearly label cables to make it easier to identify and troubleshoot specific connections.
Environmental Considerations
Consider the environment in which your branch cables operate.
(1)Temperature Control: Ensure that cables are not exposed to extreme temperatures that could cause insulation to degrade.
(2)Moisture Prevention: Use moisture-resistant cables in humid environments to prevent corrosion and damage.
Scheduled Audits
Conduct regular audits of your cabling infrastructure. This could involve checking for compliance with industry standards and ensuring that all cables are functioning as expected.
Conclusion
Implementing these maintenance practices will help ensure that your branch cables remain in optimal condition, extending their operational lifespan.
4. How Do Environmental Factors Affect Branch Cables?
Environmental factors play a significant role in the performance and longevity of branch cables. Here’s how they can affect cable integrity.
Temperature Extremes
Extreme temperatures can cause materials to expand or contract, potentially leading to physical damage.
(1)High Temperatures: Excessive heat can cause insulation to melt or degrade, leading to short circuits.
(2)Low Temperatures: Cold temperatures can make materials brittle, increasing the risk of cracks or breaks.
Moisture and Humidity
Exposure to moisture can lead to corrosion and electrical failures.
(1)Water Damage: Water ingress can cause short circuits and degrade insulation. Use waterproof cables in exposed areas.
(2)Humidity: High humidity levels can lead to condensation, which can damage connectors and cables.
Chemical Exposure
Cables installed in industrial environments may be exposed to chemicals that can degrade materials.
(1)Corrosive Substances: Ensure that cables are rated for use in environments where they may come into contact with chemicals.
(2)Proper Selection: Choose cables with appropriate sheathing to protect against chemical exposure.
UV Radiation
If cables are installed outdoors, UV radiation can degrade insulation over time.
(1) Protection: Use UV-resistant cables or protective coverings to extend the lifespan of outdoor installations.
Conclusion
Understanding and mitigating the effects of environmental factors is crucial for maintaining the integrity and longevity of branch cables.
5. What Innovations in Branch Cable Technology Should You Know About?
As technology evolves, so does the design and functionality of branch cables. Here are some innovations that are shaping the future of branch cable technology.
Enhanced Materials
Modern branch cables are being constructed from materials that offer better durability and performance.
(1)Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH): These materials minimize toxic smoke emissions in case of fire, making them safer for use in buildings.
(2)Improved Insulation: Newer insulation materials offer better resistance to temperature extremes and chemical exposure.
Smart Cables
The rise of smart technology has led to the development of smart cables that can monitor their condition in real-time.
(1)Integrated Sensors: These cables can detect faults, measure temperature, and alert users to potential issues before they become serious.
(2)Data Monitoring: Smart cables can provide real-time data on performance metrics, helping in proactive maintenance.
Modular Designs
Modular branch cables allow for easier upgrades and repairs.
(1)Interchangeable Components: This design enables users to replace only the faulty section of a cable rather than the entire unit, reducing downtime and costs.
(2)Flexible Configurations: Modular designs allow for customized setups based on specific operational needs.
Eco-Friendly Innovations
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, manufacturers are developing eco-friendly branch cables.
(1)Recyclable Materials: Some manufacturers are using recyclable materials in their cable designs, reducing environmental impact.
(2)Sustainable Production Practices: Innovations also focus on reducing waste and energy consumption during manufacturing.
The above is a brief introduction of Occam Power Company for branch cables, if you are interested in cables and other products, you can follow our blog knowledge. We will continue to update relevant information
Conclusion
Staying informed about innovations in branch cable technology can help you make better purchasing decisions and ensure that your network infrastructure remains cutting-edge.
References
1.Cable test equipment and tools. (n.d.). Retrieved from fluke.com
2.Best practices for cable management. (n.d.). Retrieved from cableorganizer.com
3.Understanding environmental effects on cables. (n.d.). Retrieved from belden.com
4.Innovations in cable technology. (n.d.). Retrieved from electricalengineering.com
5.The importance of regular cable testing. (n.d.). Retrieved from networkworld.com
6.Smart cables: The future of connectivity. (n.d.). Retrieved from techradar.com
7.Environmental considerations for networking equipment. (n.d.). Retrieved from cisco.com
8.How to clean and maintain network cables. (n.d.). Retrieved from pcworld.com
9.Understanding branch cable technology. (n.d.). Retrieved from oukamucable.com