Historically, customer acquisition has taken an approach dominated by the so-called funnel—a straightforwardly linear approach to attracting, converting, and closing customers. With businesses taking precedence in the customer experience and retaining customers, however, a new challenge has emerged to compete in the funnel’s singular obsession.
- Enter the Flywheel Model: A Customer-Centric Approach toward Building Momentum, Customer Retention and Leverage Your Loyalty towards Sustainable Growth. I look forward to learning some detailed information about the flywheel from where it precisely derives the energy and momentum that comes towards its implementation with business: enter the detailed review related to the traditional funnels’ method.
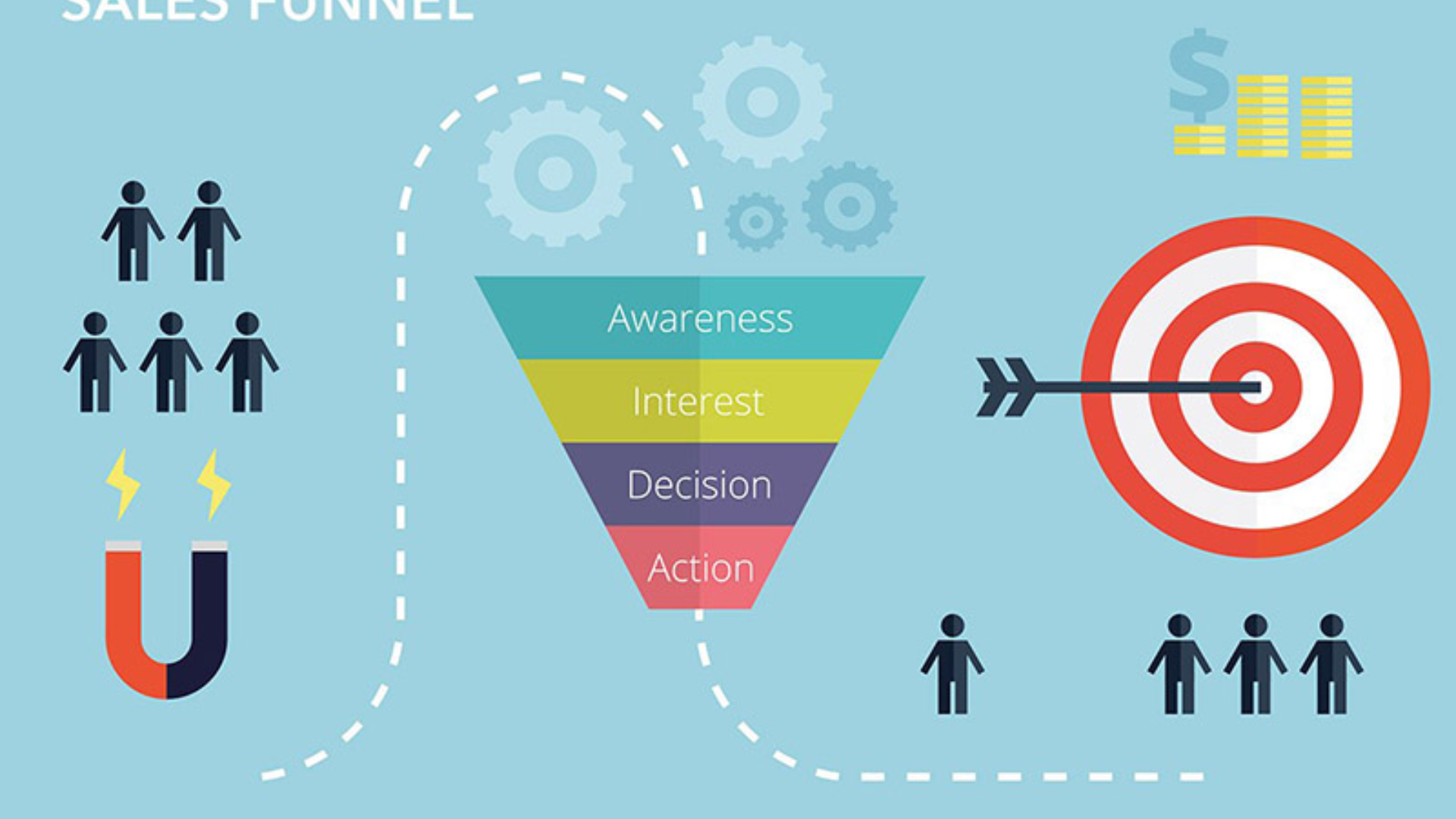
- For many years, the marketing and sales funnel has been the framework used for customer acquisition strategies. It is easy to conceptualise and visualise, as it represents the narrowing process in which prospects become customers.
Steps of the Funnel
There are generally three stages in a funnel that have come to be known as TOFU, MOFU, and BOFU, or the Top, Middle, and Bottom of the Funnel:
- Awareness (TOFU): At the most superficial level, marketers attract potential customers by generating interest via content, advertising, and campaigns.
- MOFU:- In this stage, prospects are involved further by researching, demo attendance, or signing up for free trials.
- Decision (BOFU): This is the most minor stage. Here, leads get converted into paying customers by finalising the purchase.
The Funnel’s Limitations
While the funnel has pushed marketing success for decades, it is increasingly considered adequate for today’s customer-centric environment. The root of the problem? It ends with “purchase.” The customer lifecycle doesn’t conclude after a sale; it’s where it begins. Companies obsessed with customer acquisition miss opportunities to retain and grow relationships with existing customers.
The Flywheel Model
Unlike the linear funnel, which ends at the customer stage, the flywheel is cyclical, featuring dynamic, self-sustaining momentum where customers become part of the growth process.
What is the Flywheel?
HubSpot popularised the flywheel model as an alternative framework in growth drivers. This model focuses on customers as the axis of business momentum. The circular model revolves around three connected stages:
- Attract (like the top of the funnel): Ingratiate leads through marketing programs and great content.
- Engage like the middle of the funnel: Build trust through excellent customer service, solutions, or counselling.
- Delight: Transmute customers into advocates with every experience well above expectations.
How the Flywheel Differs from the Funnel
However, The significant difference lies in how the flywheel embeds the customer experience into all parts of the business. The funnel places the customer at the “end,” while the flywheel positions them at the centre. The happy, satisfied customers create momentum—propelling growth through reviews, referrals, and repeat purchases.
Benefits of the Flywheel Model
Switching to a flywheel model may require a mindset shift, but the benefits outweigh the costs. Here’s why companies are leaning into this approach.
- Retention Over Acquisition
It is said that acquiring a new customer costs five times more than retaining an existing one. The flywheel encourages businesses to focus on retention through delighting customers, long-term value, and higher LCV.
- Customer Advocacy & Referrals
Happy customers are your best marketers. The flywheel is focused on delighting customers so much that they refer others, which leads to organic growth. Nielsen says that 92% of consumers trust recommendations from friends and family more than any other form of advertising. 3. Sustainable Growth
Since the flywheel is built on the momentum of existing customers and does not depend solely on new leads, it is a sustainable strategy for businesses. Companies can scale without wasting money on marketing or sales by optimising every turn of the wheel.
- Customer-Centric Strategy
The flywheel keeps businesses aligned with what matters most—customer needs. Deeper connections and improved user experience grow customer loyalty exponentially.
Implementing the Flywheel Model
Transitioning to the flywheel involves vital steps to align your team and processes around this new strategy.
- Refocus Business Goals on the Customer
Starting with the flywheel involves a shift in goals. Move beyond acquisition metrics and prioritise retention, satisfaction, and customer lifetime value.
- Map the Flywheel to Your Business
Evaluate how your organisation engages with customers at every flywheel stage (Attract, Engage, Delight). Is your marketing team reaching the right audiences? Are your salespeople providing value? Is your customer service team responsive and proactive?
- Departmental Silos Must Fall
The flywheel must function as one cohesive system that integrates marketing, sales, and customer support to seamlessly share insights and customer data to create consistent, impactful experiences.
- Customer Feedback
Collect and act on customer feedback. Tools such as the Net Promoter Score (NPS) or customer satisfaction surveys provide actionable insights on refining your approach. 5. Leverage Technology Use software tools like CRM systems and marketing automation platforms to create smoother interactions, deliver personalised messaging, and track which actions delight your customers.
Case Studies
Real-world examples prove the flywheel’s effectiveness.
- HubSpot: The company that made the flywheel famous has seen tremendous growth through inbound marketing and creating delightful customer experiences. They have successfully turned their customers into evangelists, propelling brand awareness.
- Slack: With Slack’s flywheel approach focusing on making the user experience delightfully simple and engaging, this is how product design and user adoption have fueled retention and referral rates to levels unmatched by any other.
- Amazon: Relentless customer obsession is what has made Amazon the giant of the world. Fast shipping, easy returns, and personalised recommendations have repeatedly kept customers hooked and returning.
Challenges and Considerations
Transitioning to a flywheel is challenging. Some of the most common include legacy systems, resistance to change, or gaps in cross-functional collaboration.
How to Overcome Challenges:
- Begin with something small, starting with an immediate impact that you make on one phase of the flywheel.
- Encourage a culture of experimentation across teams.
- Highlighting the internal wins can help demonstrate the power of the flywheel to stakeholders.
Building Momentum, One Turn at a Time
To stay competitive and foster sustainable growth, businesses today must move beyond the funnel mindset. Adopting the flywheel model will enable you to turn your customers into your greatest asset and build a brand that thrives on loyalty, retention, and advocacy.
It’s time to rethink how you’re growing your business. Are you ready to build your flywheel?