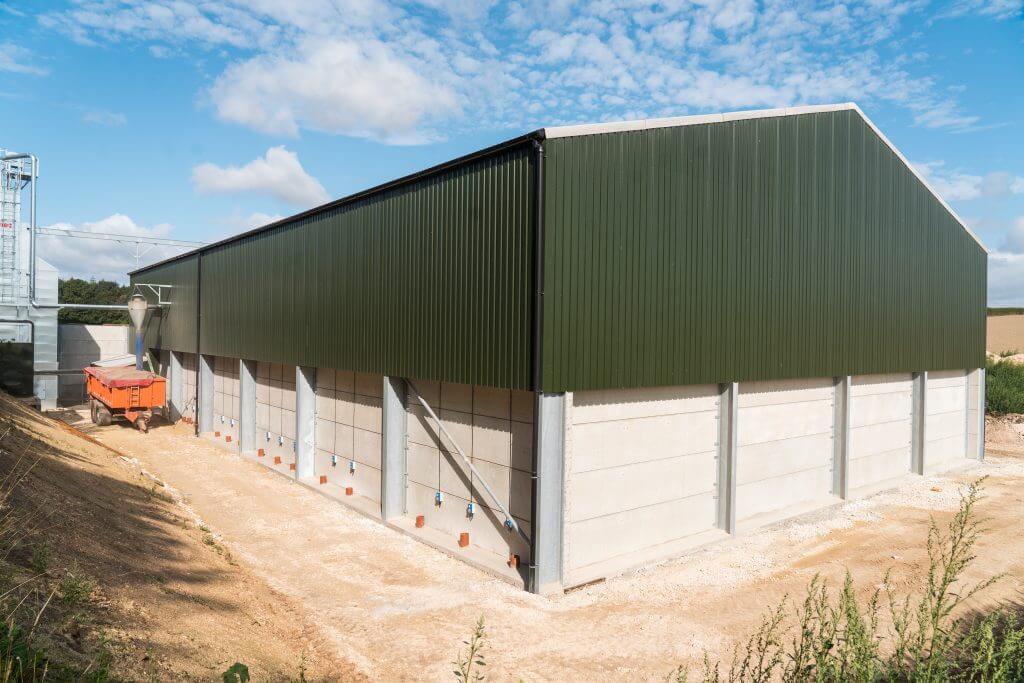
When constructing reinforced concrete retaining walls in the UK, adherence to safety guidelines and compliance with British Standards (BS) are of utmost importance. These standards ensure that the walls are designed, constructed, and maintained to meet safety requirements and provide structural stability. In this article, we will discuss the safety aspects associated with the different types of reinforced concrete retaining walls commonly used in the UK and emphasise the importance of adhering to relevant British Standards.
Gravity Retaining Walls
Gravity retaining walls rely on their self-weight to resist the lateral forces exerted by the retained material. During construction, several safety aspects should be considered:
BS 8002:2015 – Code of Practice for Earth Retaining Structures: This standard provides guidance on the design and construction of gravity retaining walls. Adhering to this standard ensures that the walls are designed with appropriate factors of safety, taking into account the characteristics of the soil and the imposed loads.
Stability Analysis: Prior to construction, a thorough stability analysis should be carried out to assess the wall’s capacity to resist the lateral forces. The analysis should consider factors such as soil properties, groundwater conditions, and potential surcharge loads.
Construction Materials: All materials used in the construction of gravity retaining walls should comply with the relevant British Standards for concrete and reinforcement. This ensures the quality and durability of the materials, contributing to the long-term stability of the structure.
Drainage System: A proper drainage system should be incorporated to control groundwater behind the wall. British Standards related to drainage systems, such as BS EN 1295-1:2020, should be followed to ensure effective water management and prevent hydrostatic pressure buildup.
Cantilever Retaining Walls
Cantilever retaining walls utilise the principles of leverage to resist lateral forces. Safety aspects associated with the construction of cantilever retaining walls include:
BS 8002:2015 – Code of Practice for Earth Retaining Structures: This standard provides guidance on the design and construction of cantilever retaining walls. Adhering to this standard ensures that the walls are designed with appropriate factors of safety and consideration of soil properties.
Formwork and Falsework: Proper design, installation, and bracing of formwork and falsework are crucial for the safety of workers and the stability of the structure. Compliance with BS EN 12812:2019 – Falsework – Performance Requirements and General Design is essential to ensure the strength and stability of the formwork system.
Reinforcement Installation: The correct placement and fixing of reinforcement bars should follow the specifications outlined in BS 8666:2005 – Specification for Scheduling, Dimensioning, Bending, and Cutting of Steel Reinforcement for Concrete. Adhering to this standard ensures that the reinforcement is accurately positioned, providing the necessary strength and integrity to the wall.
Backfilling and Compaction: Backfilling behind the wall should be carried out in accordance with BS 8002:2015 and BS 5837:2012 – Trees in relation to design, demolition and construction – Recommendations. Proper compaction techniques, using suitable equipment, should be employed to avoid excessive pressure on the wall and ensure the stability of the retained material.
Counterfort Retaining Walls
Counterfort retaining walls provide additional stability through the inclusion of counterforts at regular intervals along the wall. Safety aspects related to the construction of counterfort retaining walls include:
BS 8002:2015 – Code of Practice for Earth Retaining Structures: Adhering to this standard ensures that the design and construction of counterfort retaining walls are in line with established safety principles.
Formwork and Falsework: Similar to cantilever walls, proper design, installation, and bracing of formwork and falsework are essential to prevent collapse during construction. Compliance with BS EN 12812:2019 is necessary to ensure the stability and strength of the formwork system.
Counterfort Reinforcement: The placement and fixing of reinforcement bars in the counterforts should adhere to BS 8666:2005. Proper positioning and anchoring of the reinforcement ensure the structural integrity and stability of the counterforts.
Backfilling and Compaction: Backfilling and compaction techniques should comply with the requirements specified in BS 8002:2015. Careful attention should be given to avoid excessive pressure on the wall and ensure the stability of the retained material.
Tied-back Retaining Walls
Tied-back retaining walls utilise tendons or ground anchors to provide additional resistance against lateral forces. Safety aspects associated with the construction of tied-back retaining walls include:
BS 8081:2015 – Code of Practice for Ground Anchorages: This standard provides guidance on the design, construction, and testing of ground anchorages. Adhering to this standard ensures that the installation and performance of the anchors meet safety requirements.
Excavation Safety: Excavation for anchor installation should follow appropriate safety practices to prevent soil collapse or instability. Compliance with BS 6164:2019 – Code of Practice for Safety in Trenches, and other related standards, is essential to ensure the safety of workers during the excavation process.
Tendon Installation: The installation of tendons or ground anchors should be carried out by experienced professionals following the manufacturer’s specifications and design requirements. Proper tensioning and stressing of the tendons are critical to achieving the desired resistance and safety of the wall.
Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular monitoring and inspection of the tied-back retaining wall are necessary to identify any signs of distress or tendon degradation. Compliance with BS 8102:2009 – Code of Practice for Protection of Below Ground Structures against Water from the Ground is essential to ensure the ongoing safety and durability of the wall.
Conclusion
The construction of reinforced concrete retaining walls in the UK requires strict adherence to safety guidelines and compliance with relevant British Standards. Whether it’s a gravity, cantilever, counterfort, or tied-back wall, safety aspects related to excavation, construction materials, reinforcement, backfilling, drainage systems, and monitoring should be carefully considered. By adhering to British Standards, engineers can ensure the structural stability, integrity, and long-term safety of reinforced concrete retaining walls.