In any field where data is involved—whether it’s business, finance, science, or even daily life—making informed decisions is crucial. One tool that significantly aids decision-making is the concept of standard deviation. While it may sound complex, once broken down, standard deviation offers a clear insight into data variations, helping individuals and organizations make smarter, more precise decisions. This article will explore how standard deviation plays a vital role in decision-making, helping you reduce uncertainty and gain confidence in your choices.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Standard Deviation
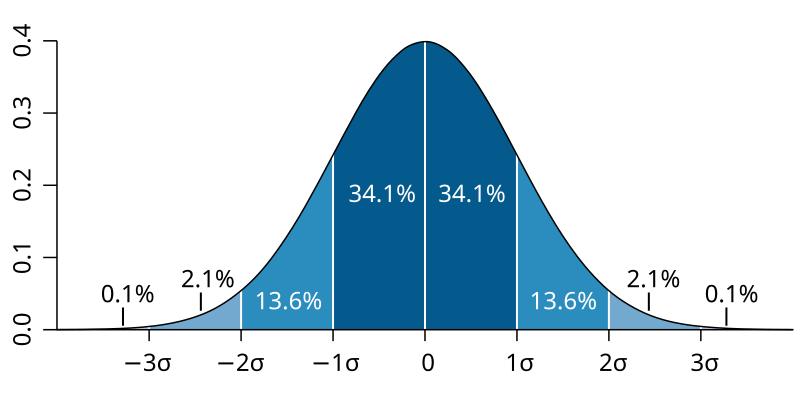
Before diving into its role in decision-making, let’s briefly explain what standard deviation is. Simply put, standard deviation is a measure of how spread out numbers are in a dataset. It shows the average distance between each data point and the mean (average) of the dataset. If the data points are close to the mean, the standard deviation is low, indicating consistency. On the other hand, a high standard deviation suggests that the data is more spread out and there is greater variability.
In decision-making, understanding how consistent or variable your data is can guide you in making the right choice. Whether you’re trying to evaluate financial risks, quality control, or project timelines, standard deviation gives you a quantitative measure of uncertainty or stability.
Making Sense of Data Variability
In decision-making, the variability of data is often as important as the mean or average. Consider a company deciding between two suppliers for a critical component. Both suppliers may offer similar prices (average cost), but one might have a much larger variation in delivery times. The supplier with lower standard deviation in delivery times is more reliable, which could lead to fewer production delays.
In this case, standard deviation reveals more than just cost—it uncovers the consistency and reliability of each supplier, giving decision-makers the insight they need to choose the supplier that will help avoid unnecessary downtime and potential losses.
Standard Deviation in Risk Management
Risk is an inherent part of decision-making. Whether it’s an investment decision or project planning, understanding risk levels is crucial for success. Standard deviation plays a key role in assessing risk, particularly in finance and investment decisions.
For instance, when evaluating two potential investments, standard deviation helps in understanding the volatility of returns. An investment with high standard deviation indicates that its returns are more spread out, suggesting higher risk. On the other hand, an investment with low standard deviation suggests that returns are more consistent and predictable, indicating lower risk.
This insight allows investors and business owners to make more informed decisions, balancing their risk appetite with potential returns. If you’re risk-averse, you might prefer investments with lower standard deviation for more predictable returns, while risk-tolerant individuals might opt for high-risk, high-reward options.
Quality Control and Consistency
In manufacturing and production environments, maintaining quality and consistency is critical. Standard deviation is widely used to monitor and control the quality of products. Companies track the variability of their production processes by measuring standard deviation, which helps identify when processes deviate from their intended target.
Let’s say a factory is producing screws, and the length of each screw needs to be 5 cm. By calculating the standard deviation of the screw lengths in each batch, managers can assess how consistent the production process is. If the standard deviation is small, it indicates the screws are consistently produced at 5 cm. If the standard deviation is large, it signals inconsistencies, and adjustments may be needed to the manufacturing process.
By using standard deviation, companies can make timely decisions to correct any issues before they become larger problems, thus ensuring product quality remains high and reducing waste or defects.
Forecasting and Planning
In business and project management, making accurate forecasts and plans is vital to success. Standard deviation helps in understanding the uncertainty in forecasting, providing decision-makers with a range of possible outcomes.
For example, if you’re a project manager tasked with estimating the time to complete a task, simply using the average time taken in the past may not be enough. By calculating the standard deviation of past project completion times, you can better understand how much variation exists in the process. This helps you anticipate delays or fluctuations, enabling you to set more realistic deadlines and allocate resources effectively.
In this case, standard deviation enhances decision-making by giving a clearer picture of potential variability, reducing the likelihood of missed deadlines and cost overruns.
Improving Customer Satisfaction
In customer service, ensuring a consistent experience can significantly impact customer satisfaction. Whether it’s delivery times, response times, or product quality, customers value consistency. Standard deviation helps businesses analyze how consistently they are meeting customer expectations.
For instance, an e-commerce company may want to ensure that it delivers orders within a promised timeframe. By calculating the standard deviation of delivery times, the company can assess whether their shipping process is reliable. A low standard deviation would indicate consistent delivery times, while a high standard deviation would suggest a need for improvement.
With this insight, businesses can make informed decisions to improve processes, leading to better customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Enhancing Decision-Making in Human Resources
Human resources (HR) departments also benefit from using standard deviation in their decision-making. Whether it’s for employee performance evaluations or salary benchmarking, understanding variability is essential.
Take employee performance as an example. HR managers may track the productivity of employees over time. By calculating the standard deviation of performance scores, HR can identify employees who are consistently high performers and those whose productivity fluctuates. This helps in making decisions about promotions, bonuses, and additional training needs.
Similarly, when deciding on salary increments or offers to potential hires, understanding the standard deviation in salaries within the industry helps HR offer competitive packages without overpaying or underpaying.
Financial Decision-Making with Standard Deviation
One of the most significant uses of standard deviation in decision-making occurs in financial analysis. Businesses and individuals alike rely on this metric to make informed decisions about investments, budgeting, and financial planning.
For example, a company may analyze the historical sales figures of its products to forecast future sales. By calculating the standard deviation of these figures, the company can estimate the likely range of sales for the coming months or years. A high standard deviation suggests significant variability, prompting caution or a more conservative approach to financial planning. A low standard deviation, on the other hand, signals predictability, allowing the company to confidently plan future investments or expansions.
In personal finance, standard deviation can help individuals make better decisions about savings and investments. It enables people to assess the risk of investment portfolios and understand how much their returns might fluctuate, guiding them toward making choices that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions with Standard Deviation
Whether you’re running a business, managing projects, making investments, or working in HR, standard deviation offers valuable insights into the variability and risk in your data. By understanding how spread out your data is, you can make more informed decisions, mitigate risks, and improve outcomes.
Standard deviation isn’t just a complex mathematical concept—it’s a practical tool that helps you reduce uncertainty and navigate the challenges of decision-making with confidence. When you can measure the variability in your data, you have the power to make smarter, more strategic choices that benefit your organization or personal endeavors in the long run.