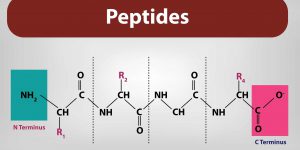
Peptides are short chains of amino acids that serve as building blocks for proteins and play essential roles in biological processes. Peptide custom synthesis allows researchers and pharmaceutical companies to create specific peptide sequences tailored to their needs. This article delves into what custom peptide synthesis is, its applications, the process involved, and key considerations.
What is Custom Peptide Synthesis?
Custom peptide synthesis is the process of artificially creating specific peptides in a laboratory setting. This capability is crucial for various fields including molecular biology, drug discovery, diagnostics, and therapeutic development. It allows scientists to study peptide functions, develop new drugs, and create diagnostic tools.
Applications of Custom Peptide Synthesis
Research: Scientists use custom peptides to explore biological processes at the molecular level. These peptides can serve as standards in assays, tools for studying protein-protein interactions, or substrates for enzymatic reactions.
Therapeutics: Customized peptides have therapeutic applications, including the development of peptide-based drugs that target specific diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and infectious diseases.
Vaccines: Peptides are being explored as potential vaccine components. Custom peptides can be designed to elicit specific immune responses.
Diagnostics: Synthetic peptides serve as vital components in diagnostic tests. They can act as antigens for antibody production or be used in assays to detect specific biomarkers.
Cosmetics: In the beauty industry, peptides are incorporated into skincare products for their purported benefits in skin repair and anti-aging.
The Process of Custom Peptide Synthesis
The process of custom peptide synthesis generally involves the following steps:
Design: The desired peptide sequence is designed based on the requirements of the study or application. Considerations of peptide design include the intended function of the peptide and physical properties such as solubility and stability.
Synthesis: Peptide synthesis is typically done using solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) or liquid-phase peptide synthesis (LPPS). SPPS is the most common method, where the peptide is assembled on a solid support and cleaved off once complete.
Purification: After synthesis, the crude peptide mixture contains not only the desired peptide but also impurities and by-products. Techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) are used to purify the peptides.
Characterization: The final step involves characterizing the synthesized peptide to confirm its identity and purity. Techniques like mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy may be employed.
Key Considerations in Custom Peptide Synthesis
Quality Control: Ensuring the quality and purity of the synthesized peptides is crucial for experimental reliability. Reputable synthesis companies should provide quality assurance measures and analytical data.
Scale of Production: Consider the scale required for your application, whether it’s milligram quantities for research or larger scales for clinical applications.
Cost: Custom peptide synthesis can be expensive, especially for longer or more complex peptides. Budget accordingly while balancing quality and quantity needs.
Modification Capabilities: Depending on the research goal, you may need peptides with specific modifications, such as phosphorylation or cyclization. Check that your synthesis provider can accommodate these requests.
Custom peptide synthesis is a powerful tool that has transformed research and therapeutic development in the life sciences. With the ability to create tailored peptides for a multitude of applications, scientists are unlocking new possibilities in understanding biological systems and treating diseases. As the field continues to evolve, advancements in synthesis technologies and techniques will undoubtedly enhance its reach and efficiency.