Cobalt is a critical metal used in a variety of industries, most notably in the production of batteries, superalloys, and catalysts. Its importance has surged in recent years due to the growing demand for lithium-ion batteries, which power electric vehicles (EVs), smartphones, laptops, and other portable electronics. As the global transition to renewable energy and electric mobility gains momentum, cobalt’s role has become even more prominent, making its price trends of great interest to industries, investors, and governments alike.
The cobalt price trend, like other commodities, is influenced by a complex set of factors, including supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical considerations, production costs, and technological advancements. This article explores the factors driving cobalt prices, historical price trends, and future projections for the global cobalt market.
Table of Contents
ToggleFactors Influencing Cobalt Prices
1. Global Demand for Electric Vehicles and Batteries
One of the primary drivers of cobalt prices is the demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and the batteries that power them. Cobalt is a key component of lithium-ion batteries, particularly in the cathode materials used in electric cars. As the global transition to electric mobility accelerates, demand for cobalt has grown substantially.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Adoption
The rapid adoption of electric vehicles, driven by global policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions, has had a significant impact on cobalt demand. Leading EV manufacturers, such as Tesla, Volkswagen, and BYD, are increasing their production capacities, which has boosted the demand for battery-grade cobalt. As EV sales continue to rise, cobalt prices are expected to remain sensitive to the pace of electric mobility adoption.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/cobalt-price-trends/pricerequest
Battery Production
The production of rechargeable batteries—used not only in EVs but also in smartphones, laptops, and renewable energy storage systems—is another major demand driver for cobalt. The energy storage market, which requires cobalt-based batteries, is expanding as renewable energy generation (such as solar and wind power) grows. This trend has created sustained demand for cobalt, pushing prices upward.
2. Supply Constraints and Production Locations
Cobalt supply is geographically concentrated, with the majority of global production coming from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), which accounts for more than 70% of global cobalt production. This concentration creates supply risks, making cobalt prices particularly vulnerable to disruptions in production and exports from the DRC.
Mining Conditions in the DRC
The mining sector in the DRC is plagued by political instability, conflict, and labor issues, which can significantly impact the global cobalt supply. Additionally, concerns over unethical mining practices, including the use of child labor, have led to pressure from governments and companies to ensure ethically sourced cobalt. These supply risks contribute to price volatility, as any disruptions in the DRC’s production capacity can create immediate shortages in the global market.
Limited Production Outside the DRC
While other countries, such as Russia, Australia, and Canada, also produce cobalt, their output is relatively small compared to the DRC. Efforts to diversify cobalt supply sources are ongoing, but it will take time to develop new mining projects in regions outside the DRC. This imbalance between demand and supply has led to fluctuations in cobalt prices.
3. Technological Advancements and Battery Chemistry Evolution
Technological innovations in battery chemistry and recycling processes can influence the demand for cobalt and, by extension, its price. Researchers and companies are actively working to reduce reliance on cobalt in batteries due to its high cost and supply risks.
Shift to Low-Cobalt and Cobalt-Free Batteries
Battery manufacturers are exploring alternative chemistries to reduce or eliminate cobalt from their batteries. For example, nickel-rich lithium-ion batteries (such as NMC 811) use less cobalt than traditional NMC 622 or NMC 532 batteries. Additionally, some companies are investing in cobalt-free battery technologies, such as lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries, which have gained popularity in certain EV segments.
While the transition to low-cobalt and cobalt-free batteries could reduce demand for cobalt in the long term, the current pace of this transition is gradual. Until these alternative chemistries become widespread, cobalt will remain an essential material in battery production, supporting strong demand and higher prices.
Battery Recycling Technologies
Cobalt recycling from used batteries is becoming an increasingly important source of supply. As recycling technologies improve and become more cost-effective, the amount of cobalt recovered from end-of-life batteries is expected to grow. This could provide some relief to the tight supply-demand balance, potentially stabilizing prices in the future.
4. Geopolitical and Trade Factors
Geopolitical events and trade policies can significantly impact cobalt prices. The concentration of cobalt supply in a few countries, combined with rising demand from key industries, has led to increased sensitivity to geopolitical developments.
Trade Restrictions and Sanctions
Sanctions or trade restrictions imposed on major cobalt-producing countries, such as the DRC or Russia, can lead to supply disruptions and price increases. For example, any sanctions on Russian metals exports could affect the global cobalt supply chain, leading to price volatility.
Strategic Stockpiling
Some countries and companies have begun to stockpile cobalt due to concerns over future supply disruptions or price spikes. Strategic stockpiling by major consumers of cobalt, such as battery manufacturers and automakers, can influence short-term demand and create upward pressure on prices.
5. Environmental and Social Regulations
Environmental and social concerns surrounding cobalt mining, particularly in the DRC, have prompted governments, companies, and consumers to push for more responsible sourcing practices. These pressures can affect the cost of production and influence the market dynamics for cobalt.
Ethical Sourcing and Certification Initiatives
The demand for responsibly sourced cobalt is growing as consumers and companies prioritize sustainability and corporate social responsibility. Initiatives such as the Cobalt Refinery Supply Chain Due Diligence Standard and the Responsible Cobalt Initiative aim to ensure that cobalt is sourced in an environmentally and socially responsible manner. However, complying with these standards may increase production costs, which could be passed on to consumers through higher cobalt prices.
Environmental Regulations
Mining regulations aimed at reducing environmental degradation can also impact production costs. For instance, stricter environmental laws in cobalt-producing regions may lead to increased investment in cleaner mining technologies, potentially driving up production costs and, consequently, the price of cobalt.
6. Energy Prices and Transportation Costs
The cost of energy and transportation plays a significant role in the overall cost of cobalt production and delivery. As cobalt mining and refining are energy-intensive processes, any fluctuations in energy prices can influence the cost of production and transportation, thereby affecting cobalt prices.
Rising Fuel and Shipping Costs
The global shipping and transportation industry has experienced significant cost increases due to rising fuel prices, port congestion, and supply chain disruptions. Higher transportation costs, particularly for cobalt sourced from remote mining locations, can drive up the cost of delivering cobalt to global markets, contributing to price increases.
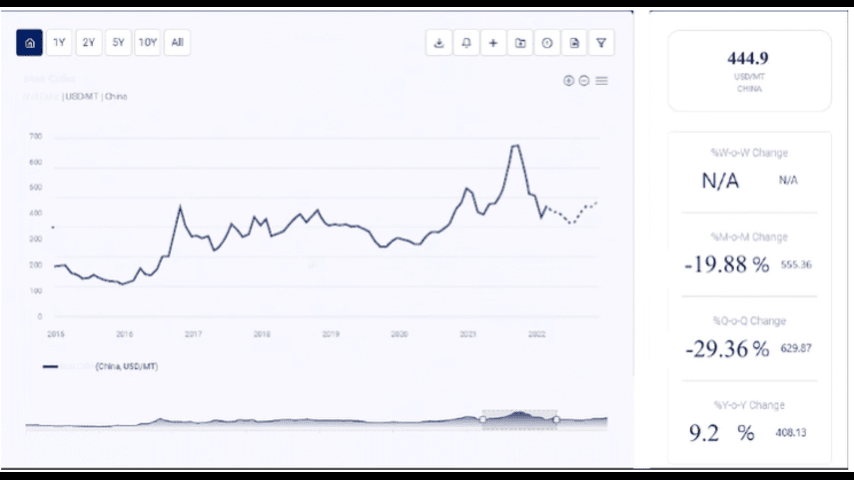
Historical Cobalt Price Trends
1. Pre-2010 Period: Steady Growth
Before 2010, cobalt prices experienced steady growth, driven primarily by demand from the aerospace and industrial sectors, where cobalt is used in superalloys and catalysts. The battery industry, while growing, had not yet reached the scale seen today. During this period, cobalt prices were relatively stable, with moderate fluctuations based on global economic conditions and industrial demand.
2. 2010-2017: Increasing Demand from Batteries and Electronics
Between 2010 and 2017, cobalt prices began to rise steadily as the demand for lithium-ion batteries, particularly in consumer electronics, increased. The growth of the smartphone, laptop, and portable electronics markets led to a surge in cobalt consumption. Additionally, the early stages of the electric vehicle revolution contributed to a gradual increase in cobalt demand.
By 2017, cobalt prices experienced a significant spike, fueled by concerns over supply shortages and the rapid expansion of the battery market. Prices peaked in 2017 as EV manufacturers ramped up production, and battery manufacturers began securing long-term cobalt supply contracts to meet future demand.
3. 2018-2019: Supply Surges and Price Declines
In 2018 and 2019, cobalt prices saw a sharp decline due to a combination of increased supply and a shift in battery chemistries. The price drop was largely driven by new cobalt mining projects coming online in the DRC, which increased global supply. At the same time, battery manufacturers began reducing the amount of cobalt used in lithium-ion batteries, favoring nickel-rich alternatives.
By the end of 2019, cobalt prices had stabilized at lower levels, reflecting a more balanced supply-demand dynamic in the market.
4. 2020-2021: COVID-19 Impact and Recovery
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on cobalt prices in 2020. During the early stages of the pandemic, global industrial activity slowed, leading to a temporary reduction in cobalt demand. Cobalt prices fell as a result of lower demand from the automotive and electronics sectors.
However, by mid-2020, cobalt prices began to recover as the global economy reopened and demand for EVs and consumer electronics surged. The pandemic also disrupted supply chains, particularly in the DRC, where mining operations faced restrictions due to health and safety concerns. This supply disruption, combined with rising demand, contributed to a rebound in cobalt prices in 2021.
5. 2022-2023: Price Surge Due to Geopolitical Tensions and Supply Chain Issues
In 2022 and 2023, cobalt prices experienced another surge, driven by geopolitical tensions, rising energy prices, and supply chain disruptions. The Russia-Ukraine conflict had a significant impact on global metal markets, including cobalt. Russia, a major producer of cobalt, faced export restrictions, which contributed to supply constraints in the global market.
Additionally, rising fuel and transportation costs, coupled with supply chain bottlenecks, pushed cobalt prices higher in 2022 and 2023.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: [email protected]
Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada — Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK — Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) — Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA