Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
The concept of urban farming has gained substantial momentum over the past decade, as cities and towns worldwide seek innovative ways to address the growing demand for food, rising environmental concerns, and limited agricultural land. Urban farming, which refers to the cultivation of food within city environments or densely populated areas, is no longer a niche activity but a booming industry contributing to food security, sustainability, and community engagement.
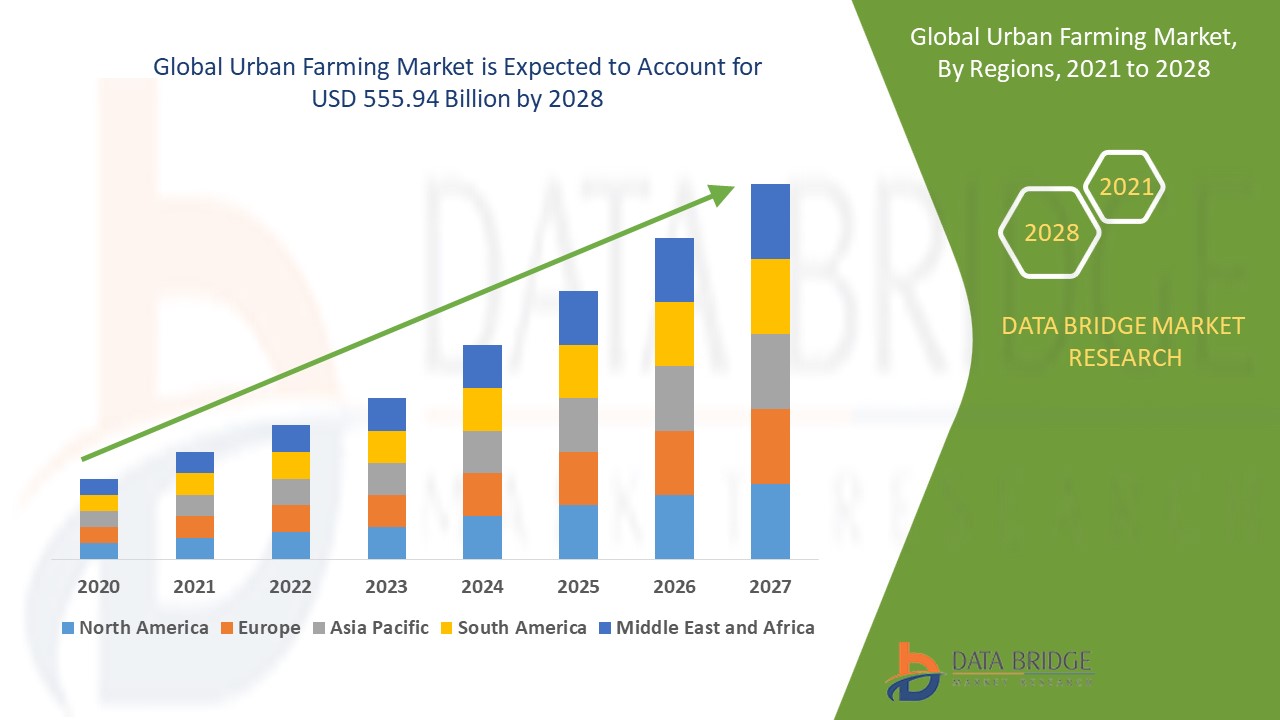
The urban farming market is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology, changing consumer preferences toward locally sourced food, and the growing awareness of environmental sustainability. As the global population continues to urbanize, with over 68% projected to live in cities by 2050, the need for efficient, sustainable, and scalable food production systems within urban environments is more critical than ever.
This comprehensive blog explores the key drivers of the urban farming market, different types of urban farming, technological advancements, benefits, challenges, and future prospects of this transformative sector.
What is Urban Farming?
Urban farming encompasses various methods of growing food in cities, such as rooftop gardens, vertical farming, hydroponics, aquaponics, and community gardens. It aims to shorten the distance between production and consumption, reducing food miles and enhancing access to fresh, locally grown produce.
Urban farming can range from small-scale community gardens and residential plots to large-scale commercial operations housed in skyscrapers or industrial buildings. It integrates agriculture into the urban fabric and is often focused on sustainability, resource efficiency, and fostering local food systems.
Key Drivers of the Urban Farming Market
Several factors are contributing to the growth and expansion of the urban farming market. Below are the primary drivers of this market.
1. Rising Demand for Fresh and Locally Sourced Food
Consumers are becoming increasingly conscious of where their food comes from and are demanding fresher, healthier, and more sustainably sourced products. Urban farming allows produce to be grown closer to consumers, reducing the need for long-distance transportation and enabling local communities to enjoy fresh produce that is often harvested on the same day.
- Examples: Farmers’ markets, urban farms supplying local grocery stores, and restaurants sourcing ingredients from rooftop gardens.
2. Growing Global Urbanization
As the world becomes more urbanized, cities are facing increased pressure to meet the food demands of their growing populations. Traditional farming methods, reliant on rural land and extensive resources, are struggling to keep up with urban food needs. Urban farming provides a solution by making use of unused or underutilized urban spaces to grow food where it is needed most.
- Examples: Vertical farms in New York, rooftop gardens in Tokyo, and indoor farms in Singapore.
3. Environmental Sustainability and Resource Efficiency
Urban farming promotes environmental sustainability by reducing the environmental footprint of food production. Traditional agriculture is associated with high water usage, deforestation, and the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Urban farming methods such as hydroponics and vertical farming often use less water, require fewer chemicals, and can recycle nutrients and waste. Additionally, urban farms can significantly reduce food transportation emissions by growing produce near urban centers.
- Examples: Vertical farms that use 90% less water than traditional agriculture, hydroponic systems recycling water, and community composting for urban gardens.
4. Technological Advancements in Agriculture
The integration of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and automation is revolutionizing the urban farming sector. These technologies help monitor and control environmental conditions, optimize resource usage, and increase yields, making urban farming more efficient and scalable. Technologies such as smart sensors, climate control systems, and data analytics are driving the commercial viability of urban farming operations.
- Examples: AI-powered vertical farms that optimize lighting and watering schedules, sensor-based hydroponic systems that monitor plant health, and automated indoor farms with robotic harvesting systems.
5. Government Initiatives and Policy Support
Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the benefits of urban farming and are implementing policies and initiatives to support its growth. These initiatives often include financial incentives, grants, and zoning regulations that encourage the establishment of urban farms in city spaces. Urban farming is also being integrated into broader sustainable urban development plans to enhance food security and reduce the environmental impact of cities.
- Examples: Incentives for rooftop gardens in Paris, subsidies for urban farms in the Netherlands, and government-funded community gardens in U.S. cities.
Types of Urban Farming
Urban farming comes in various forms, each suited to different environments and scales of operation. Below are some of the most prominent types of urban farming practices:
1. Vertical Farming
Vertical farming involves growing crops in stacked layers or vertically inclined surfaces, often in controlled indoor environments such as warehouses or skyscrapers. This method uses artificial lighting, climate control, and hydroponic or aeroponic systems to maximize space utilization and crop yield. Vertical farming is particularly suited to urban areas with limited land space and is an efficient way to produce a high volume of crops in a small footprint.
- Examples: AeroFarms in New Jersey, Sky Greens in Singapore, and Plantagon in Sweden.
2. Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a soil-free farming method that involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions. Hydroponic systems are highly efficient, using less water than traditional farming, and can be set up in urban spaces such as rooftops, greenhouses, and indoor facilities. Hydroponics is ideal for growing leafy greens, herbs, and other fast-growing crops in urban environments.
- Examples: Gotham Greens in Chicago, hydroponic farms in Dubai, and rooftop hydroponic systems in Barcelona.
3. Aquaponics
Aquaponics combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants in water) in a symbiotic system. The fish produce waste that is converted into nutrients for the plants, while the plants filter the water, which is then recirculated back to the fish tanks. Aquaponics is a sustainable farming method that allows for the production of both crops and fish in an urban setting, making it highly resource-efficient.
- Examples: Urban aquaponic farms in Milwaukee, commercial aquaponics in Australia, and small-scale aquaponic setups in urban backyards.
4. Rooftop Farming
Rooftop farming involves growing crops on the rooftops of buildings, making use of otherwise underutilized space. Rooftop farms can be found on commercial buildings, apartment complexes, and even schools. They contribute to urban greening, improve air quality, and reduce the heat island effect in cities. Rooftop farms can range from small community gardens to large commercial operations supplying local markets.
- Examples: Brooklyn Grange in New York City, Lufa Farms in Montreal, and The Farmhouse rooftop garden in Bangkok.
5. Community Gardens
Community gardens are shared spaces where individuals and families can grow their own food in small plots. These gardens often serve as community hubs, promoting social interaction, education, and food security. Community gardens can be found in vacant lots, parks, and other public spaces, and they play a key role in improving access to fresh food in urban areas, particularly in food deserts.
- Examples: P-Patch Community Gardens in Seattle, Incredible Edible Todmorden in the U.K., and City Farms in Sydney.
Benefits of Urban Farming
Urban farming offers numerous benefits that extend beyond food production. These benefits impact the environment, public health, local economies, and communities.
1. Increased Food Security
Urban farming helps address food security challenges by increasing access to fresh, locally grown produce. In densely populated areas, particularly food deserts, urban farms can provide affordable and nutritious food to residents who may otherwise lack access to fresh options.
2. Environmental Sustainability
Urban farming reduces the environmental impact of food production by cutting down on transportation emissions, conserving water, and minimizing the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. Additionally, urban farms can help reduce the urban heat island effect, improve air quality, and promote biodiversity in cities.
3. Economic Development and Job Creation
Urban farming can contribute to local economic development by creating jobs and supporting local businesses. From small-scale farmers and greenhouse operators to companies specializing in urban agriculture technologies, the sector offers diverse employment opportunities. Additionally, urban farms can stimulate local economies by attracting tourists, hosting events, and selling produce to local restaurants and markets.
4. Community Engagement and Education
Urban farms often serve as educational platforms, teaching city residents about sustainable agriculture, healthy eating, and environmental stewardship. They provide spaces for community engagement, volunteerism, and social interaction, fostering a sense of community and connection to nature in urban environments.
5. Mental and Physical Health Benefits
Access to green spaces and nature has been shown to improve mental health and well-being. Urban farms provide city dwellers with opportunities to engage in physical activity, reduce stress, and experience the therapeutic effects of gardening. These benefits are particularly important in urban areas where green spaces may be limited.
Challenges Facing the Urban Farming Market
Despite its growth and potential, the urban farming market faces several challenges that must be addressed to ensure its continued success.
1. High Initial Investment and Operating Costs
Urban farming often requires significant upfront investment in infrastructure, technology, and labor. Vertical farms, for example, need specialized equipment such as LED lighting, climate control systems, and automation, which can be expensive to install and maintain. Securing funding and achieving profitability can be a challenge for urban farming startups and small businesses.
2. Limited Space and Zoning Regulations
Finding suitable space for urban farms can be difficult, especially in densely populated cities with high real estate costs. Additionally, zoning regulations and land-use policies may restrict the development of urban farms in certain areas, limiting their growth potential.
3. Energy and Resource Requirements
While urban farming methods such as vertical farming and hydroponics are resource-efficient, they often rely on artificial lighting, climate control systems, and other technologies that require substantial energy inputs. Ensuring that urban farming operations are energy-efficient and sustainable is critical to their long-term success.
4. Scaling and Commercial Viability
While small-scale urban farms can be successful in providing local produce to communities, scaling these operations to meet the demands of larger urban populations is a challenge. Urban farming businesses need to find ways to scale efficiently while maintaining profitability and sustainability.
Future Prospects and Trends in Urban Farming
The future of urban farming looks promising, with continued innovation and investment driving the market forward. Below are some key trends shaping the future of urban farming.
1. Integration with Smart Cities
Urban farming is expected to play a significant role in the development of smart cities, where technology and data are used to optimize urban living. Smart cities will integrate urban farms with other sustainable infrastructure such as renewable energy systems, water recycling, and waste management, creating a more resilient and self-sufficient urban ecosystem.
2. Increased Adoption of Automation and AI
Automation, robotics, and AI will continue to transform urban farming, making operations more efficient and reducing labor costs. Autonomous robots that can plant, monitor, and harvest crops, along with AI-powered systems that optimize resource usage, will enable urban farms to scale and meet the demands of urban populations.
3. Expansion of Vertical and Indoor Farming
As cities continue to grow and space becomes even more limited, vertical and indoor farming will expand. These farms will be housed in repurposed industrial buildings, shipping containers, and even high-rise skyscrapers, maximizing space utilization in urban environments. The development of more efficient and cost-effective technologies will make vertical farming more accessible to a broader range of cities and regions.
4. Collaboration with Local Governments and Corporations
The urban farming market is likely to see increased collaboration between local governments, corporations, and non-profit organizations. Public-private partnerships will help fund and support urban farming projects, while corporations may incorporate urban farming into their sustainability initiatives. Additionally, urban farms could be integrated into corporate campuses, schools, and hospitals, providing fresh food and educational opportunities.
Conclusion
Urban farming is rapidly transforming the way we produce and consume food, offering a sustainable and innovative solution to the challenges of global urbanization, food security, and environmental sustainability. By integrating agriculture into the urban fabric, urban farming is reshaping cities, creating greener, more resilient communities, and providing fresh, locally grown produce to urban populations.
As technological advancements, government support, and consumer demand for sustainable food systems continue to grow, the urban farming market is poised for significant expansion. From vertical farms in skyscrapers to community gardens in vacant lots, urban farming represents a vital component of the future of agriculture and urban living.
The future of urban farming holds great promise, and its continued evolution will play a crucial role in addressing the food challenges of the 21st century, while promoting a more sustainable, healthy, and connected urban environment.