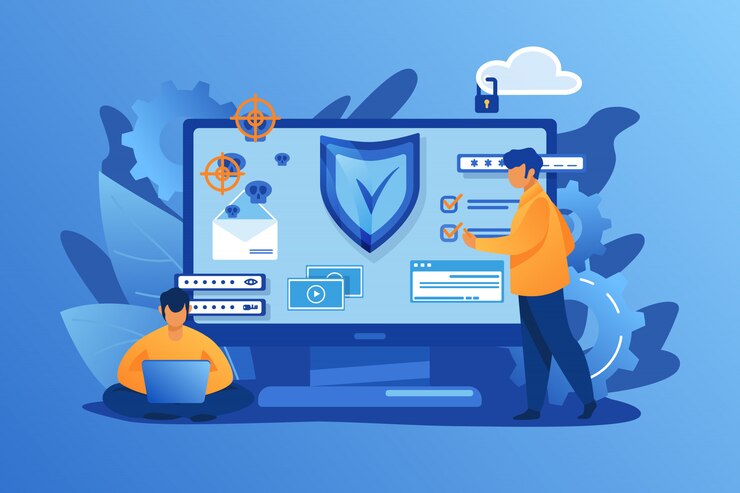
In today’s interconnected world, the concept of cybersecurity risk management has become more critical than ever. With cyber threats constantly evolving, organizations face immense pressure to protect their sensitive data and IT infrastructure. Managing cybersecurity risks is no longer an optional task; it is a fundamental necessity for businesses seeking to safeguard their digital assets and ensure long-term resilience. This article delves into the importance of cybersecurity risk management, key frameworks, and best practices organizations can adopt to mitigate risks in the modern threat landscape.
Why Cybersecurity Risk Management Matters
The shift to digital has transformed the way businesses operate, but it has also expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and phishing schemes can cause significant financial and reputational damage. According to a report from IBM, the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million in 2023. As these threats escalate, it’s critical for organizations to prioritize cybersecurity risk management to avoid catastrophic losses.
Cybersecurity risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with the use of technology and the internet. Effective risk management strategies help organizations reduce the likelihood of successful cyberattacks, minimize damage when attacks occur, and recover quickly from incidents. This approach integrates security policies and controls into all business processes, ensuring that cybersecurity is considered at every level of decision-making.
Core Elements of Cybersecurity Risk Management
Effective cybersecurity risk management requires a multi-layered approach, combining people, processes, and technology to create a resilient defense system. Below are the key elements that every cybersecurity risk management strategy should incorporate:
1. Risk Assessment
A thorough risk assessment is the foundation of any cybersecurity risk management program. During this process, organizations identify and evaluate the potential risks to their IT infrastructure, data, and operations. This involves mapping out the attack surface, identifying vulnerabilities, and understanding how threats could exploit those weaknesses.
Risk assessments should be conducted regularly, as new threats and vulnerabilities emerge over time. Moreover, the results should inform all subsequent risk management activities, including the selection of security controls and policies.
2. Risk Mitigation
After identifying risks, organizations need to implement controls to mitigate those risks. This may include deploying advanced firewalls, encryption technologies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and other security measures to protect sensitive data and systems. Risk mitigation strategies also involve employee training programs, which help ensure that staff members understand their role in maintaining cybersecurity.
Additionally, patch management and system updates are critical to reducing vulnerabilities in software and hardware. Organizations must establish processes to promptly apply patches and updates, closing security gaps that cybercriminals might exploit.
3. Incident Response
Even with strong preventive measures in place, no organization is immune to cyberattacks. A well-designed incident response plan is essential for minimizing damage when attacks occur. Incident response teams should be trained to quickly detect, assess, and contain security breaches, as well as to recover from incidents as swiftly as possible.
Post-incident analysis is also crucial for identifying lessons learned and implementing improvements to prevent future attacks. Organizations should regularly test and update their incident response plans to ensure they remain effective as new threats emerge.
4. Continuous Monitoring
Cybersecurity is not a one-time task—it requires continuous monitoring and improvement. Advanced threat detection tools, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, can help organizations monitor their networks in real time and identify potential threats before they cause damage.
In addition to monitoring internal systems, organizations should keep an eye on emerging cyber threats, such as zero-day vulnerabilities and newly developed attack methods. Threat intelligence services can provide valuable insights into the latest cyber risks, enabling organizations to adjust their defenses accordingly.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance
In addition to protecting their assets, businesses must also navigate a complex regulatory landscape. Governments worldwide are enacting stricter data privacy laws and cybersecurity regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and legal penalties, as well as reputational damage.
To ensure compliance, organizations must integrate cybersecurity risk management into their overall governance frameworks. This includes conducting regular audits, documenting risk management activities, and maintaining a record of security controls.
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has also heightened its focus on cybersecurity. In 2023, the SEC introduced new rules requiring public companies to disclose material cybersecurity incidents and outline their risk management strategies. These regulations underscore the growing importance of cybersecurity risk management in the financial sector and beyond.